Home Gensets: Your Guide to Reliable Power Solutions

Intro
In today's world, the need for reliable power sources has never been more critical. Home generator sets, commonly known as gensets, serve as a vital solution during power outages. Their importance extends beyond mere convenience; they are essential for maintaining normal household operations during unforeseen electrical disruptions. Understanding the different types, mechanisms, and practicalities of home gensets can empower individuals, particularly farmers and agricultural enthusiasts, to make informed decisions about their power needs.
Topic Overview
Home gensets are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, providing backup power for homes. They come in various sizes and types, making them suitable for diverse applications. In the realm of agriculture, ensuring a continuous power supply is crucial for operations such as irrigation, heating, and equipment running. Having gensets readily available can mitigate losses caused by energy interruptions.
- Definition of Key Terms
- Relevance in Agriculture
Home generator sets find their significance notably in agriculture, horticulture, and agronomy. Reliable electricity is critical for powering irrigation pumps, agricultural machinery, and climate control systems in greenhouses. This consistent power ensures that crops receive sufficient water and necessary environmental conditions, ultimately safeguarding productivity and crop yield.
- Generator Set (Genset): A combination of an engine and a generator used to generate electrical power.
- Power Outage: A temporary suspension of electrical service due to faults in the distribution network.
- Continuous Power Supply: An uninterrupted provision of electrical power that is essential for operational stability.
Current Trends and Innovations
As technology advances, home gensets evolve to meet the changing demands of users. Increased efficiency and sustainability are now more prioritized, reflecting the global push towards cleaner energy solutions.
- Recent Advancements in the Field
Manufacturers are focusing on enhancing fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and integrating smart technology features. Such improvements can lead to lower operational costs and a smaller environmental footprint. - Emerging Technologies and Practices
New hybrid systems that combine solar panels and traditional gensets are gaining traction. This integration allows users to benefit from renewable energy while having reliable backup from conventional power sources when needed.
Practical Applications
Understanding how to effectively utilize home generator sets can significantly impact their performance and longevity. Practicing best methods can optimize their benefits.
- Step-by-Step Guides or How-Tos
- Tips and Best Practices for Implementation
- Select the Right Generator: Assess your power needs to choose an adequately sized genset. Consider running and starting wattages to ensure it meets all electrical demands.
- Proper Installation: Engage a qualified technician to ensure safe and compliant installation. Proper grounding and fuel connection are critical for operational safety.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine checks. It includes changing the oil, replacing filters, and testing the battery. This helps prolong the lifespan of the genset.
- Always keep a supply of fuel on hand to avoid potential shortages during emergencies.
- Familiarize yourself with the generator's operation manual for optimal use.
- Consider noise levels in residential areas; some models offer quieter operation, which can be beneficial in community settings.
"Gensets are not merely appliances; they are lifelines during uncertainties."
Moreover, the environmental impact of gensets must also be considered. While providing essential power, it is vital to balance their usage with eco-friendly practices to minimize the carbon footprint.
Foreword to Home Gensets
Home generator sets, commonly known as gensets, play an important role in modern households, especially in areas prone to power interruptions. They offer a dependable source of energy during outages, ensuring that essential appliances and systems continue to function. This reliability makes gensets not just a luxury but often a necessity for many families.
By understanding what home gensets are, their historical evolution, and contemplating their practical utility, consumers can make informed decisions about selecting the right unit for their needs. The increasing unpredictability of weather patterns, alongside global energy concerns, underscores the significance of home power solutions. Hence, it is critical to investigate various facets of home gensets to appreciate their value thoroughly.
Definition and Purpose
Home gensets are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. They provide additional electricity when the main power grid fails or is insufficient. The primary purpose of these devices is to ensure that homes can maintain essential functions during power outages. This can include keeping refrigerators running, powering heating systems, or even supporting complete home systems depending on the capacity of the genset.
The functionality of gensets varies based on their type, fuel consumption, and output. Many households favor convenience and efficiency, hence understanding these aspects is paramount for making a good purchase.
Historical Context
The concept of generating electric power on-site is not a novel idea. In the late 19th century, homes began using small-scale generators to power lights and other devices, paralleling advances in electrical engineering. Over the decades, developments in fuel technology and energy efficiency significantly shaped the design and use of gensets. Early models were largely dependent on steam or water power.
By the mid-20th century, internal combustion engines became the cornerstone of generator technology. Today’s generators utilize various fuel sources including gasoline, propane, diesel, and even natural gas, reflecting how consumption patterns and energy policies have shifted over the years. In parallel, the increasing need for cleaner energy solutions prompted more innovation in this area, giving rise to hybrid and solar-powered models, which are gaining popularity in recent times.
Thus, understanding the historical context of home gensets provides insights into not just their physical characteristics but also their integration into modern living and energy strategies.
Types of Home Gensets
Home generator sets come in various types, each tailored to specific needs and scenarios. Understanding these types is vital for optimizing the use of gensets in your home. Choosing the right generator ensures reliability during outages and can significantly enhance household convenience. Each generator type has different capacities, fuel usages, and installation processes. Thus, it is crucial to carefully evaluate your requirements before selecting one.
Portable Generators
Portable generators are compact, versatile, and easy to transport. They are ideal for temporary power needs, such as during camping trips, events, or short-term power outages at home. Their mobility is one of their strongest benefits. However, their power output ranges from 1,000 to 10,000 watts, making them suitable primarily for smaller appliances and tools.
In terms of operation, portable generators often use gasoline. This can be advantageous because gasoline is widely available. They typically have a pull-start mechanism, making them user-friendly. Although these generators are not meant for long-term use, they can provide sufficient power for essential appliances like refrigerators, fans, and lights when necessary.
"When selecting a portable generator, understanding its wattage capability is essential to match your power needs."
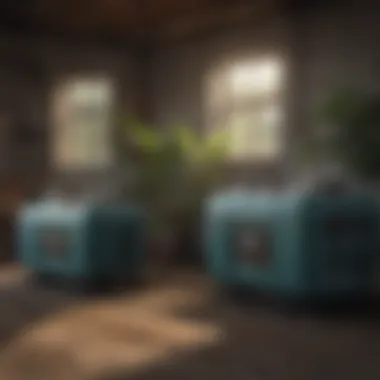

Standby Generators
Standby generators provide a permanent solution for power outages. They are installed directly on the premises, often connected to the house’s electrical system. In contrast to portable generators, standby generators kick in automatically when the main power source fails. This feature makes them particularly appealing for people who prioritize convenience and reliability.
Typically fueled by natural gas or propane, these generators have a larger power capacity, ranging from 5,000 to 20,000 watts. This allows them to cover all household needs, sustaining multiple appliances and systems simultaneously. Their installation requires professional services, which is a consideration for potential buyers. However, their peace of mind during long outages is worth the investment.
Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are a newer technology in the genset market. They differ from conventional generators due to their ability to provide clean electricity. This feature makes them suitable for sensitive electronic devices, such as laptops and smartphones, which could be damaged by voltage spikes.
The power output of inverter generators can range widely, usually from 1,000 to 4,000 watts. One significant advantage is their fuel efficiency. They adjust the engine speed to match the power demand, resulting in lower fuel consumption. This efficiency makes them an attractive option for people looking to minimize fuel expenses.
Inverter generators are also quieter than traditional generators, making them suitable for residential areas where noise could be an issue. Their portability allows users to take them on camping trips or use them at home during power disruptions.
Understanding these types of home gensets allows consumers to make better-informed decisions according to their unique power requirements and situational needs. An informed choice may lead to improved satisfaction and enhanced preparedness for unexpected outages.
Operational Mechanisms
Understanding the operational mechanisms of home generator sets is critical for anyone considering their use. This knowledge provides insight into how generators function, what fuels they utilize, and how each element contributes to their efficiency and effectiveness in supplying power. By grasping the mechanics behind these systems, users can optimize their performance, enhance safety, and make informed choices regarding maintenance and operation.
How Generators Work
Generators operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When the generator's engine runs, it spins a rotor within a magnetic field. This spinning motion generates an electric current. The key components involved include the alternator, engine, fuel system, voltage regulator, and cooling system. Together, these parts ensure the generator produces electricity efficiently and safely.
The alternator plays a central role, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. The engine provides the power needed to turn the alternator. As the engine combusts fuel, it generates the energy necessary to create electricity. The output is then managed by the voltage regulator, maintaining a stable voltage level for the devices connected to the generator. Lastly, the cooling system prevents the generator from overheating during operation.
Fuel Sources
Various fuel sources power home generators, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the differences can aid in selecting the right type for specific needs.
Gasoline
Gasoline is a common choice for many portable generators. It is widely available, making it convenient for users. The ease of fueling these generators makes gasoline popular among homeowners. However, gasoline generators often suffer from poor fuel shelf-life. They can also be less efficient and more polluting compared to other fuel options. Users should also consider the storage requirements due to gasoline's flammability.
Propane
Propane is another viable option that comes with some benefits. It burns cleaner than gasoline, which contributes to less environmental pollution. Propane also has a longer shelf-life, making it a preferred choice for emergency preparedness. Additionally, propane systems can be more efficient, providing substantial energy with less waste. On the downside, the initial setup for propane systems may be more complex, requiring additional equipment such as tanks and lines.
Natural Gas
Natural gas generators offer continuous power availability if connected to a gas line. This fuel source provides stable energy pricing and is incredibly efficient. Natural gas is cost-effective and has lower emissions than gasoline or diesel. However, its use requires consistent access to gas lines, which may not be viable for all homeowners. Dependability on gas supply can also be a concern in emergencies.
Diesel
Diesel generators are favored for their longevity and durability. They generally provide more power output and can run longer on a single tank compared to gasoline options. Diesel fuel itself is often more affordable, depending on the region. However, noise levels of diesel generators can be a drawback, as they tend to be louder. Additionally, diesel emissions are comparatively higher, raising environmental concerns.
Choosing the right fuel source for a generator is fundamentally linked to the application, availability, and specific needs of the user. Understanding these mechanisms ensures better decision-making when selecting a generator.
Selection Criteria
Selecting the right home generator set is a crucial process, especially for agriculture farmers and enthusiasts who rely on power for various operations. This selection involves multiple aspects, each contributing to the overall effectiveness and value of the genset. Understanding these criteria can help in making an informed decision that meets specific needs and ensures long-term satisfaction.
Power Requirements
The first aspect to consider is the power requirements. It is essential to determine what devices and systems will need electricity during an outage. This typically involves calculating the wattage of essential equipment, such as water pumps, refrigeration units, and lighting systems. Each device has a starting and running wattage requirement, which must be understood clearly.
Farmers should prioritize appliances that are non-negotiable during a power failure. Make a detailed list and sum up the total wattage to ensure the selected genset can handle the load. Additionally, considering future expansions in equipment or needing additional power for seasonal operations will also play a role in determining the appropriate generator capacity.
Budget Considerations
The budget for a home generator set varies significantly based on the type, power output, and additional features. Establishing a clear budget from the beginning can help narrow down options. Aside from the initial purchasing price, consider long-term operating costs which may include fuel consumption, maintenance, and possible repairs.
Sometimes, a higher initial investment can lead to cost savings over time due to greater efficiency and lower fuel usage. Evaluate financing options if necessary, as many suppliers offer payment plans or financing solutions to help spread the initial cost.
Noise Levels

Another vital consideration is the noise levels produced by the generator. Noise can become a significant issue in rural areas where quiet operation may be preferred. Understanding the decibel levels of different units can lead to a better living and working environment. In addition to being mindful of personal comfort, decreasing noise can also help in maintaining a good relationship with neighbors and livestock.
Look for models specifically designed to operate quietly. Inverter generators usually offer reduced noise and can be a suitable choice for those sensitive to sound. Reading user reviews and manufacturer specifications will provide valuable insights into noise output.
"Choosing the right generator means understanding the needs of your farm and the realities of your budget."
Considering these selection criteria as a whole provides a framework for making an informed decision. It ensures that the genset chosen will serve its intended purpose effectively and efficiently for years to come.
Installation Processes
Understanding the installation process for home generator sets is crucial. A well-executed installation enhances the generator's longevity and operational efficiency. Moreover, it ensures safety for users and minimizes risks associated with improper connections or setups. This section elucidates the essential steps in the installation process, which include site assessment, obtaining necessary permits, and successful electrical connections.
Site Assessment
Before proceeding with installation, an in-depth site assessment is essential. This step involves evaluating the location where the generator will be installed. Factors to consider include:
- Proximity to Fuel Source: Ensure the generator is close to the fuel supply, be it propane tanks or natural gas lines. This minimizes the cost of fuel lines and potential hazards.
- Space Availability: The area must accommodate the generator while allowing sufficient clearance for maintenance and ventilation. Typically, at least three feet of clearance from buildings and structures is a standard requirement.
- Ground Stability: A level surface is necessary for installation. An unstable ground can lead to vibrations that affect the generator's operation.
A thorough site evaluation can prevent issues during and after installation. To maximize efficiency, it is best to document all observations made during this assessment.
Permits and Regulations
Navigating permits and regulatory requirements is a significant step that cannot be overlooked. In many areas, local regulations dictate where and how generators can be installed. Here are some key considerations:
- Local Codes: Check local building codes and zoning laws, which vary significantly between regions. Some laws may restrict generator placement due to noise or safety concerns.
- Health and Safety Regulations: Compliance with health and safety standards is critical. This includes ensuring the installation follows electrical safety codes and environmental guidelines.
- Permit Applications: Some installations require permits. Contact local authorities or a building inspector to find out what is necessary in your area and apply accordingly. Failing to secure needed permits can result in heavy fines or even the requirement to undo the installation.
A meticulous approach to permits and regulations can streamline the installation process and safeguard the homeowner legally.
Electrical Connections
Electrical connections are the final aspect of the installation process, and they must be executed with precision. Correct electrical hookups ensure that the generator functions safely and efficiently. Consider the following:
- Wiring Types: Use the appropriate wiring gauge per the electrical load calculations. This ensures that the generator can deliver consistent power without overheating.
- Transfer Switch Installation: A transfer switch is vital for safely interconnecting the home wiring with the generator. It prevents back-feeding into the grid, an action that poses a risk to utility workers and can damage home electronics.
- Testing: After making all electrical connections, testing the setup is important. Run the generator to ensure all circuits are powered correctly and any potential issues are addressed before regular use.
Proper electrical connections ensure safety and functionality, reducing the risk of incidents during operation.
Maintenance and Safety
Maintaining home generator sets is critical for their longevity and performance. Regular maintenance ensures that the generator functions efficiently when needed most, particularly during power outages. Additionally, safety is paramount in avoiding accidents and potential hazards associated with improper use or installation. Failure to attend to maintenance can lead to inefficient operations, which may increase fuel consumption. It can also result in wear and tear, reducing the lifespan of the equipment.
Proper awareness around maintenance and safety practices allows users to prevent costly repairs and ensure reliability. Some critical elements in this area include routine checks, adherence to guidelines, and understanding the common pitfalls.
Routine Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance affects both the performance and reliability of home gensets. Consider these essential tips to keep your generator in optimal condition:
- Inspect Oil Levels: Check the oil regularly and change it as recommended by the manufacturer. Low oil levels can cause damage to the engine.
- Clean Air Filters: Dirty air filters can lead to engine inefficiency, so cleaning or replacing them is necessary for maintaining airflow.
- Test the Battery: A healthy battery is vital to a generator’s start function. Test the battery regularly and replace it at the first signs of wear.
- Run the Generator Periodically: Running the generator monthly for about 30 minutes can prevent the buildup of stale fuel and keeps the engine lubricated.
- Check Fuel Levels: Ensure that there is enough fuel in the generator, especially before storms or predicted outages.
Implementing these tips can dramatically improve the performance of the genset. Users will find that taking a few simple preventive steps can save considerable time and expense.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Even with diligent maintenance, issues may still arise. Recognizing these problems quickly can mitigate serious concerns. Here are some frequent issues with home generators and how to troubleshoot them:
- Generator Won't Start: If a generator does not start, check the fuel level, ensure the battery is charged, and verify that the ignition switch is in the ON position.
- Unusual Noises: Strange noises may indicate loose parts. Inspect the generator to tighten or replace any components that seem faulty.
- Inconsistent Power Supply: Fluctuations in power could suggest a problem with the voltage regulator. Consult the manual to troubleshoot or consider professional help.
- Excessive Vibrations: If the generator experiences vibrations, check for level placement and ensure it rests on a stable surface.
- Fuel Leaks: Any signs of fuel leakage should be taken seriously. Disconnect the generator immediately and consult a technician.
By understanding common issues associated with home gensets, users can maintain equipment effectively and prevent disruptions in power supply. Performing regular checks and having a solid troubleshooting guide empowers users to manage their gensets confidently.
"Regular maintenance not only enhances performance but also plays a significant role in ensuring safety."
These practices, when implemented consistently, will enhance the overall efficiency and safety of your home generator, offering peace of mind during critical moments.
Environmental Considerations


The importance of environmental considerations in the context of home generator sets cannot be overstated. As households increasingly rely on gensets for power during outages, understanding their environmental footprint becomes essential. Home gensets contribute to energy autonomy, but they also have implications for air quality, noise levels, and resource consumption. Therefore, a thoughtful approach to selecting and using these devices can lead to better outcomes for both users and the environment.
Impact of Fuel Choice
The choice of fuel significantly impacts the environmental footprint of home generators. Different fuels have varying effects on emissions and resource depletion. For instance, gasoline-powered generators are often associated with higher levels of carbon monoxide and particulate matter compared to those using propane or natural gas. Diesel generators, while efficient, can also produce higher emissions. Choosing cleaner fuels can help mitigate these environmental impacts.
- Gasoline: Common and readily available but contributes to significant air pollution.
- Propane: Burns cleaner than gasoline or diesel; lower emissions make it a preferred choice for eco-conscious users.
- Natural Gas: Abundant and cleaner, it emits fewer greenhouse gases, making it more environmentally friendly.
- Diesel: Often more fuel-efficient but can lead to significant pollution if not properly managed.
It is also important to consider the overall efficiency of the generator model itself. Newer technologies often offer improved fuel efficiency, which can reduce not only costs but also environmental impact.
Sustainability Practices
Adopting sustainable practices when using home gensets helps minimize their ecological footprint. Here are some fundamental strategies:
- Regular Maintenance: Keeping the generator in top shape ensures it runs efficiently. Regular oil changes and air filter replacements can decrease harmful emissions.
- Use During Off-Peak Hours: Operating generators during off-peak hours can alleviate stress on the electrical grid and reduce pollution from centralized power generation.
- Consider Hybrid Systems: Some combinations of solar power and generator use can offset electricity consumption. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels and promotes renewable energy.
- Optimize Load Management: Running the generator only when necessary and managing the loads can significantly cut down on fuel consumption and emissions.
"By choosing cleaner fuels and implementing sustainable practices, homeowners can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of their home generator systems."
Cost and Economic Factors
Understanding the financial aspects of home generator sets is crucial for making informed decisions, especially for agriculture farmers and enthusiasts who often rely on consistent power for their operations. The cost considerations not only include the initial investment but also the long-term operating costs associated with maintaining and using these generators. Evaluating these factors can help in choosing the right model that aligns with budgetary constraints while also meeting power needs effectively.
Initial Investment
The initial investment for a home generator typically varies based on its type, size, and features. Generators can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on capacity and technology.
When selecting a generator, consider the following elements:
- Type of Generator: Portable generators generally cost less than standby generators, which are a permanent solution.
- Power Output: Higher wattage generators will usually have a higher price point.
- Brand and Model: More reputable brands may have a premium price due to reliability and service support.
- Installation Costs: Especially for standby generators, professional installation can add significantly to the initial cost.
It is essential to prepare a budget that encompasses not only the purchase price but also these additional costs. This foresight can prevent unexpected financial burden once the generator is needed.
Long-term Operating Costs
Once the generator is purchased and installed, ongoing costs must be factored into the economic equation. Long-term operating costs typically include fuel expenses, maintenance, and repairs. Here are important points to keep in mind:
- Fuel Expenses: The type of fuel used affects cost. For instance, diesel may be more economical than gasoline, yet propane can offer a cleaner burn. Evaluate local fuel prices and availability for each option.
- Routine Maintenance: Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance. This could involve changing oil, replacing air filters, and inspecting major components. Consider allocating a small budget annually for maintenance services.
- Repair Costs: Over time, components may need repairing or replacing due to wear and tear. It is wise to factor in a potential expense for repairs, or consider warranty options at the time of purchase.
"Investing in a home generator is not just about the upfront cost, but understanding how it will fit into your long-term budget strategy."
Technological Innovations
Technological innovations in home generator sets represent a significant shift in how power is generated and managed in residential settings. As global dependency on reliable electricity grows, the integration of advanced technology within generators has enhanced both their functionality and accessibility. Homeowners today can enjoy more efficient, robust, and sophisticated systems designed to respond automatically to power disruptions.
Smart Generator Technology
Smart generator technology is revolutionizing the concept of home energy production. These systems utilize digitally-controlled mechanisms powered by IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities. This integration allows generators to communicate with other connected devices in the household, providing real-time data on energy usage and generator status. For instance, a smart generator can automatically turn on during a blackout and switch off once utility power restores.
This technology significantly reduces the need for manual operation, therefore minimizing the risk of human error and enhancing safety. Additionally, the data collected can help homeowners make informed decisions regarding energy consumption, ultimately promoting efficiency. Notably, devices such as the Generac Guardian Series have gained traction among homeowners for their reliability and ease of integration with smart home systems.
Remote Monitoring Systems
Remote monitoring systems provide another layer of convenience and security for managing home gensets. These systems enable users to monitor generator performance and status remotely via smartphone applications or web interfaces. Homeowners can receive alerts about low fuel levels, maintenance reminders, or operational malfunctions, even when they are away from home.
Such capabilities not only enhance user experience but also ensure timely maintenance. They can prevent costly repairs by alerting owners to issues before they escalate. For instance, a remote monitoring system can significantly increase peace of mind for families who live in areas prone to power outages. By allowing users to monitor their generators efficiently, this technology supports uninterrupted power supply and aligns with the increasing demand for smart and self-service home solutions.
Ending
The conclusion serves as a vital segment in this discourse on home generator sets. It encapsulates the central themes discussed throughout the article, reinforcing the practical significance of home gensets in today’s tumultuous energy landscape. Households face increased uncertainties regarding power supply due to extreme weather, infrastructure issues, and other unforeseen events. Thus, understanding home generators becomes not just enlightening but essential for many.
Future of Home Gensets
The future trajectory of home generator technology appears to be one of innovation and increasing utility. Advancements in smart technology will allow homeowners to monitor and control their generators remotely, integrating them seamlessly into home energy management systems. This development enhances efficiency and provides real-time data on power consumption and availability.
As sustainability becomes a more pressing issue, manufacturers are likely to focus on producing more eco-friendly gensets. Innovations may include hybrids powered by renewable energy sources or improvements to traditional fuel efficiency. Homeowners should keep abreast of these changes to select generators that align with environmental goals while also meeting their energy needs.
Furthermore, with the rising proliferation of electric vehicles, integrating charging stations powered by home generators could become a common feature. This shift will expand the functionality of home gensets beyond mere backup power, making them integral to everyday living.
Final Thoughts
Home gensets are more than just a safety net; they represent a proactive approach towards energy management. For agriculture farmers, a dependable power supply is critical for operations like irrigation and livestock management. Therefore, investing in a home generator set ultimately empowers households to maintain continuity, resilience, and improved quality of life in unpredictable circumstances. Ensuring your home is equipped with the right generator is not just an investment in a device, but an investment in peace of mind.



